Python is a high-level, interpreted programming language known for its simplicity and readability. It is widely used for:
- Web development (using frameworks like Django and Flask)
- Data analysis and machine learning (using libraries like Pandas, NumPy, TensorFlow)
- Automation and scripting
- Software development and prototyping
- Game development, network servers, and more
Key Features:
- Easy to read and write
- Dynamically typed (you don’t need to declare variable types)
- Extensive standard library
- Large community and support
- Cross-platform (runs on Windows, Linux, macOS, etc.)
Python was created by Guido van Rossum and first released in 1991.
Here are some Python programs:
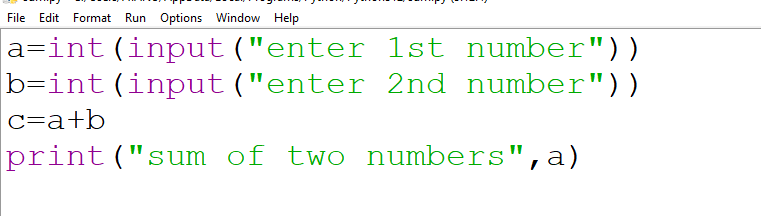
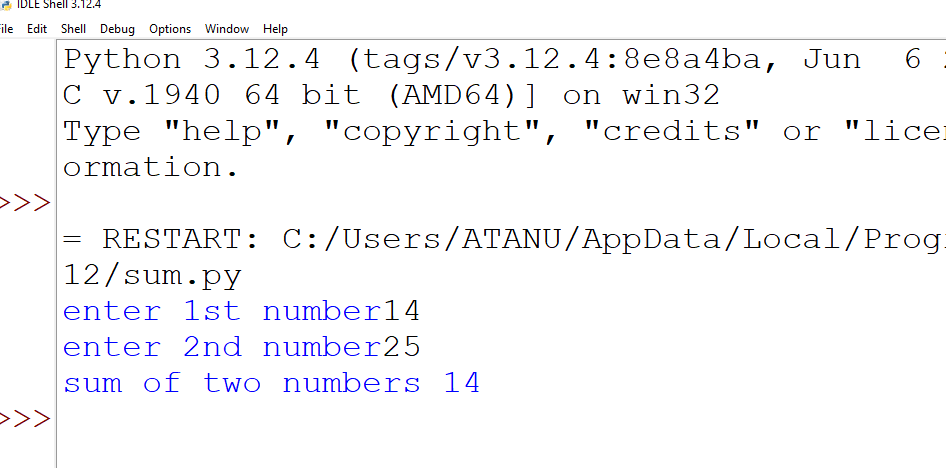
1. Write a program to accept 2 numbers from the user and print their sum.
output:
Explanation:
a = int(input("enter 1st number"))
input("enter 1st number"): Displays the message “enter 1st number” and waits for the user to type something.int(...): Converts the input string to an integer.- The resulting value is stored in the variable
a.
b = int(input("enter 2nd number"))
- Same as above, but for the second number.
- The value entered is stored in the variable
b.
c = a + b
- This adds the two integers stored in
aandb. - The result (sum) is stored in the variable
c.
print("sum of two numbers", a)
- This line prints “sum of two numbers” followed by the value of
a.
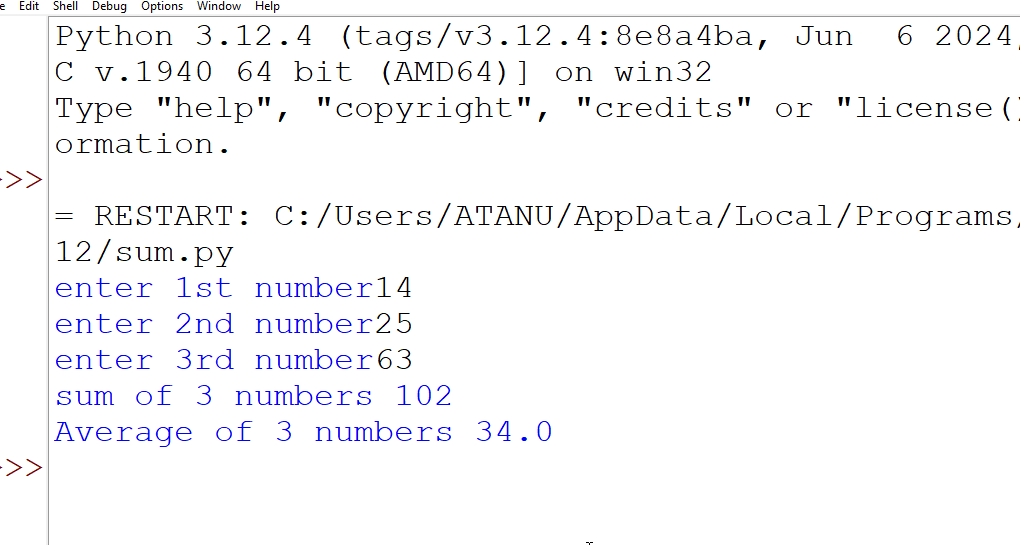
2. Write a program to accept 3 numbers from the user and print their sum and average.

Output:
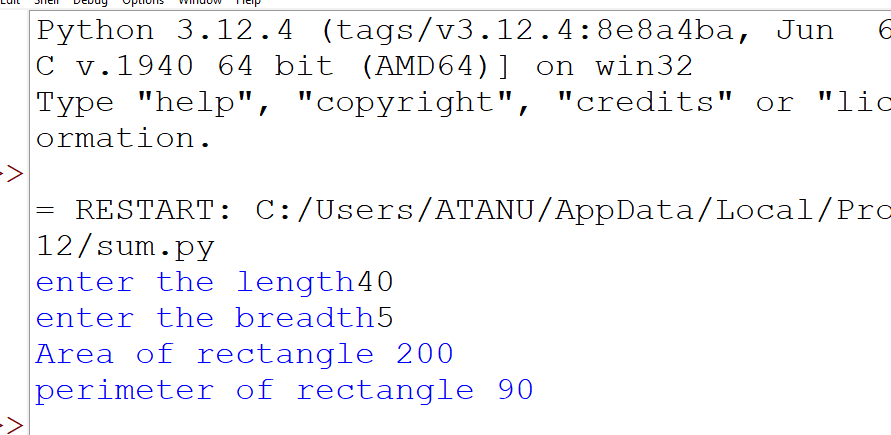
3. Write a program that accepts the length and breadth of a rectangle and prints the area and perimeter.

Output:
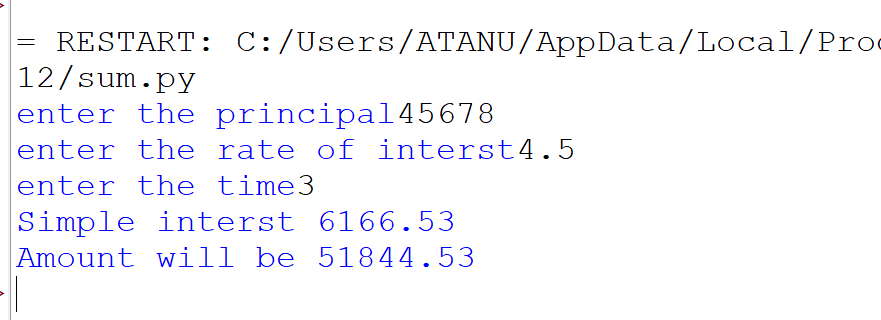
4. Write a program to accept principal, rate of interest, and time, and calculate and print the simple interest and amount.

Output:
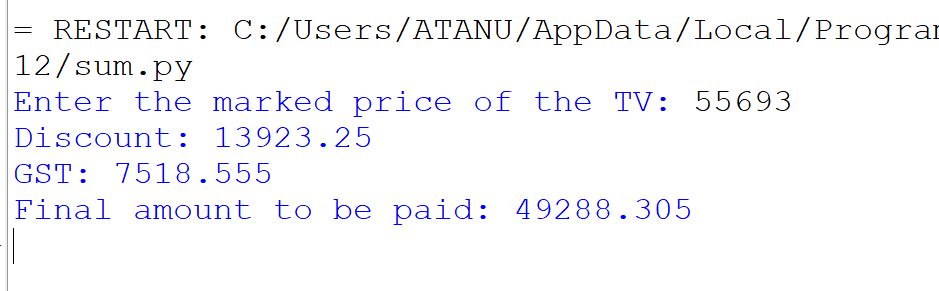
5. A shopkeeper offers a 25% discount on the marked price and includes 18% GST on an Android TV. Write a program to accept the TV price, calculate and print the discount, GST, and the final amount to be paid.

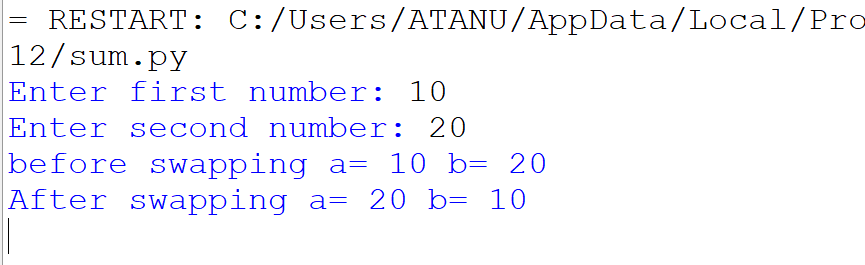
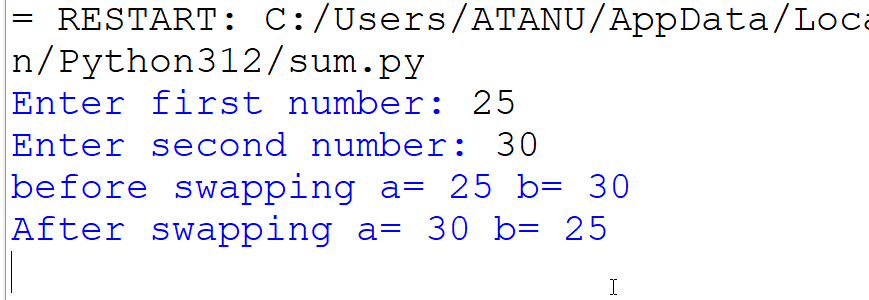
6. Write a program to accept two numbers from the user and swap them by using 3rd variable.

Output:
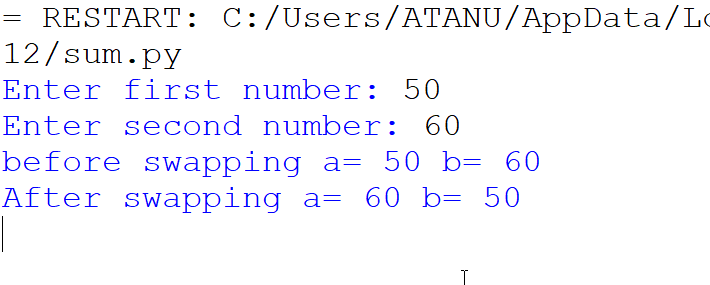
7. Swapping without using 3rd variable.

Output:
8. Another logic of swapping. By using multiple assignments.

Output:
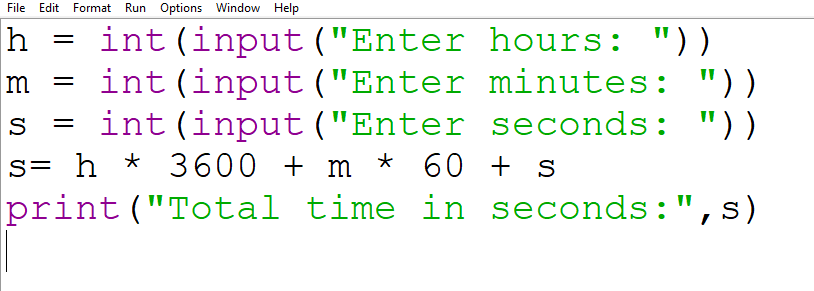
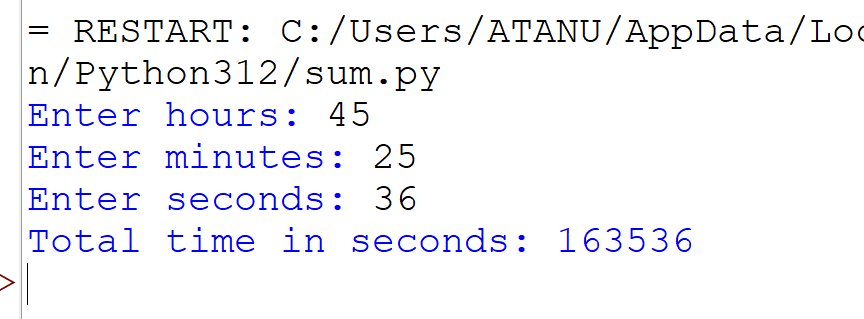
9. Write a program to accept a time in hours, minutes, and seconds and convert it into seconds only.
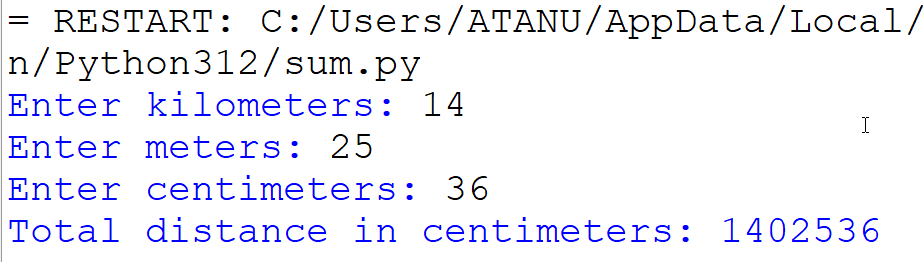
10. Python program to accept a distance in kilometers, meters, and centimeters, and convert the total distance into centimeters only.

11. Python program to accept time in seconds and convert it into hours, minutes, and seconds format.
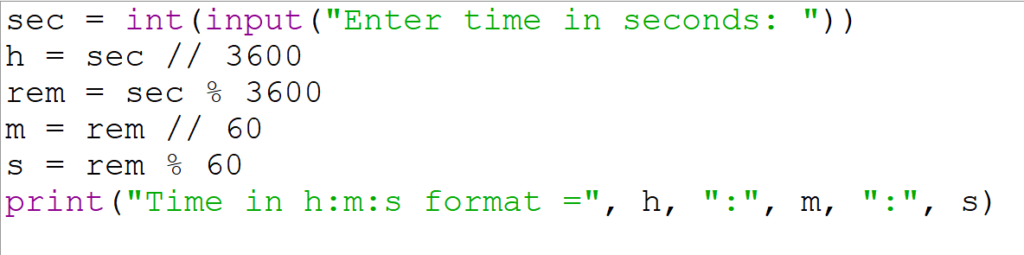

Explanation:
h = sec // 3600
3600seconds = 1 hour.- This line calculates how many whole hours are in the given seconds.
//is integer (floor) division. For example:3672 // 3600gives1.
rem = sec % 3600
%is the modulus operator, which gives the remainder after dividingsecby3600.- This gives the leftover seconds after accounting for full hours.
m = rem // 60
- From the remaining seconds, we calculate how many full minutes there are.
// 60gives integer minutes.
s = rem % 60
- The leftover seconds that couldn’t be grouped into a full minute.
- So now we have:
h= full hoursm= full minutess= remaining seconds
print("Timein h:m:s format =", h, ":", m, ":", s)
- This prints the final time in hour:minute: second format.
11. In Python, * and ** They are arithmetic operators, but they perform different operations:
- (Asterisk) – Multiplication Operator
• Used to multiply two numbers.
Example:
a = 4 * 3
print(a) - # Output: 12
** (Double Asterisk) – Exponentiation Operator
• Used to raise a number to the power of another number.
• That is, a ** b means “a raised to the power b” or a^b.
Example:
b = 2 ** 3
print(b) # Output: 8 (because 2 × 2 × 2 = 8)

